Cornea and External Diseases
The cornea is a transparent, avascular, watch-glass like structure. It forms anterior 1/6th of the outer fibrous coat of eyeball.
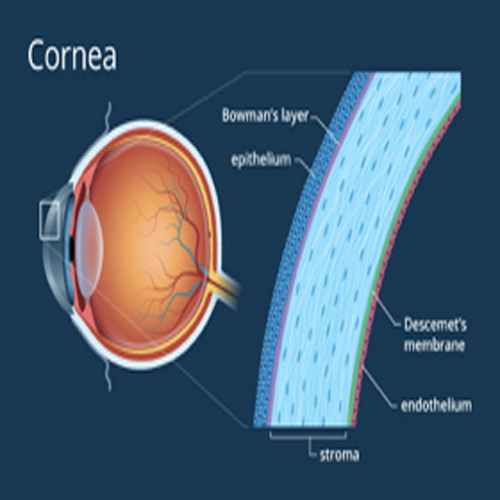
Functions
- Major refracting medium
- Protects intraocular contents
Diseases of Cornea
A. Congenital Anomalies
- 1. Megalocornea
- 2. Microcornea
- 3. Cornea Plana
- Bilaterally the cornea is comparatively flat in this condition.
- 4. Congenital Cloudy Cornea
- Cloudiness in the cornea since birth due to generally :
- Sclerocornea
- Tears in Descemet’s membrane
- Ulcer
- Metabolic Condition
- Posterior corneal defect
- Endothelial dystrophy
- Dermoids
The inflammation of cornea is called keratitis
- 1. Morphological Classification
- a. Ulcerative Keratitis (corneal Ulcer)
- b. Non-Ulcerative Keratitis.
- 2. Etiological Classification
- a. Infective keratits
- Bacterial
- Viral
- Fungal
- Chlamydial
- Protozoal
- Spirochaetal
- b. Allergic Keratitis
- Phlyctenular keratitis
- Vernal keratitis
- Atopic keratitis
- c. Trophic Keratitis
- Exposure keratitis
- Neuroparalytic keratitis
- Keratomalacia
- Atheromatous Ulcer
- d. Associated with diseases of skin and mucous membrane
- e. Associated with systemic collagen vascular disorders
- f. Traumatic keratitis
- g. Idiopathic keratitis
- Mooren’s Corneal Ulcer
- Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis
- Thygseon’s superficial punctuate keratitis
- a. Infective keratits

It happens when normal corneal cells undergo some degenerative changes due to age or some pathological condition.
- Classification
- Age related degenerations
- Arcus senilitis
- Vigt’s white limbal girdle
- Hassal-Henle bodies
- Mosaic degeneration
- Pathological degenerations
- Fatty degeneration
- Amyloidosis
- Calcific degeneration
- Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
- Furrow degeneration
- Spheroidal degeneration
- Pellucid marginal degeneration
- Terrien’s marginal degeneration
- Mooren’s Ulcer
Corneal Dystrophies
These are inherited disorders in which the cells have some inborn defects due to which cornea becomes hazy with the passage of time. There is no associated systemic pathology.
- Classification
- Anterior Dystrophies
- Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy
- Reis-Buckler’s Dystrophy
- Meesman’s Dystrophy
- Recurrent Corneal Erosion Syndrome
- Stocker-Holt Dystrophy
- Stromal Dystrophies
- Lattice Dystrophy
- Crystalline Dystrophy (Schnyder’s)
- Granular Dystrophy (Groenounw’s type I)
- Macular Dystrophy (Groenouw’s type II)
- Posterior Dystrophies
- Cornea Gutta
- Fuch’s late hereditary endothelial dystrophy
- Posterior polymorphous dystrophy (of Schlichting)
- Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy(CHED)




